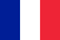
In this article, we will consider the main types of foot fungi.
All fungal infections are collectively referred to as fungal diseases. Experts divide them into two major categories-onychomycosis and dermatomycosis. In the first case, microorganisms penetrate under the nails, in the second case, the skin is affected. In addition, considering the pathogens and main symptoms of the disease, absolutely classify all types of foot fungi.
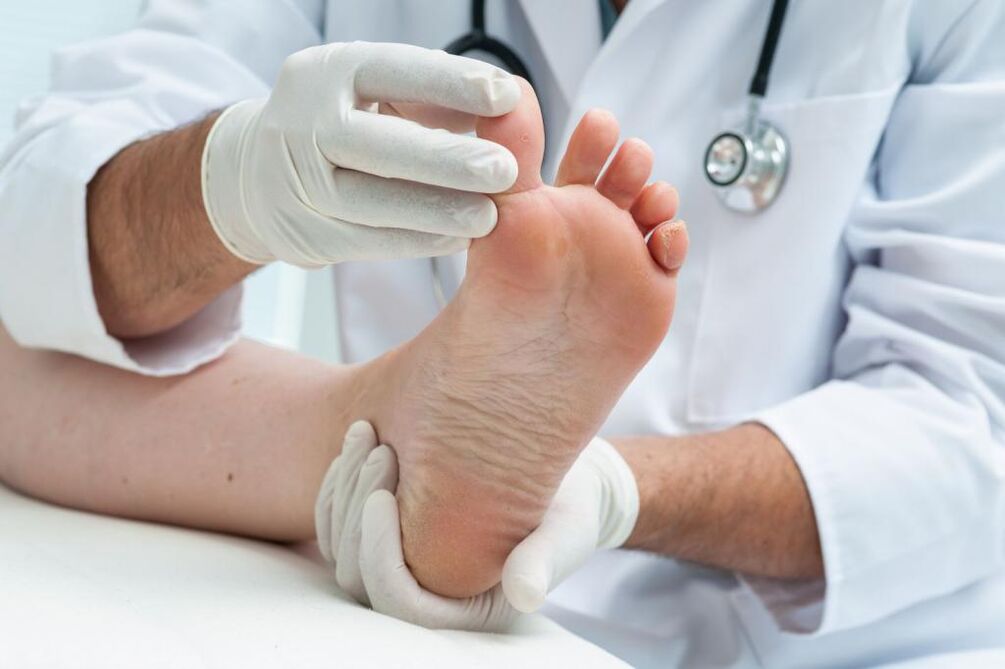
Main species
First, the type of fungus that affects the legs depends on the pathogen of the disease. Pathogenic microorganisms are divided into several categories: dermatophytes, yeasts and molds. They can cause the following common pathologies:
- Onychomycosis;
- Candidiasis;
- Epidermophytosis;
- Red algae.
The latter is a general term for a group of pathologies that affect the feet. All diseases are also divided into several groups according to clinical manifestations: membranous, moccasin-like, and blisters.
We will consider the types, photos, and treatment of foot fungus through the following alternative methods.
Red algae
The second name for this disease is erythromycosis. It is characterized by overcrowding, dryness and severe flaking of blood vessels. For people who are infected, the pathology develops very slowly and almost unknowingly.
Foot fungus in the form of bubbles is very unpleasant.
The first signs are itching and flaking, which have become apparent in the later stages of the disease. Nail damage can also occur at this stage. On the surface, the disease appears as blisters, scabs, plaques, and pustules, which are located on the entire surface of the sole. When a large number of plaques and bubbles appear, people begin to feel pain when walking.
Determining the type of foot fungus (pictured) plays a key role in the treatment. Before the treatment of erythrophysis, it is necessary to conduct a microscopic examination and study the clinical manifestations. Use an exfoliating (stratum corneum) agent to eliminate the lesions. In most cases, these are ointments and creams based on salicylic acid. Treatment is usually complicated. Antifungal drugs are prescribed at the same time as external drugs.
If the condition is severe, you should start taking the medicine in pill form. Lesions of the nail plate are treated by removing them with emollients.
This type of foot fungus (see picture above) is highly contagious. It is enough to touch things used by an infected person. If a person sweats too much, the immune system is weakened, and the feet suffer any damage, the chance of infection increases many times.
The pathogen of this disease is the fungus Tr. Trichophyton mentagrophytes. It can penetrate into the granular layer and stratum corneum of the skin, spread and cause allergies and other types of serious reactions:
- Soreness, burning and itching when walking;
- Deformation and yellowing of nails;
- The appearance of scabs, scales, painful cracks;
- Skin erosion (impregnation);
- The appearance of pustules, edema;
- A vesicle rash with a dense outer shell.
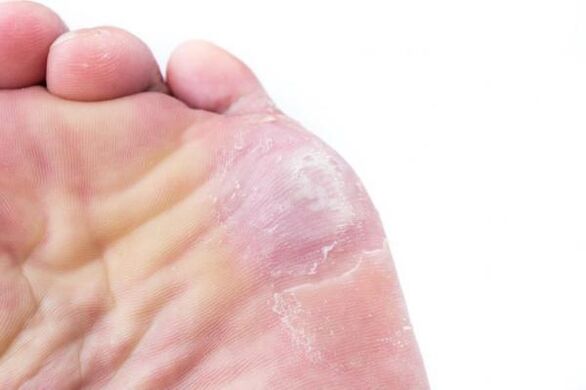
The diagnosis of this type of foot fungus includes the study of external signs and clinical manifestations. If the pathological cause is not obvious, clinical research may be required, such as examining the scratches under a microscope.
The treatment of acute erythrophytonosis includes the use of drugs based on 0. 25% silver nitrate, 10% calcium, and 1% m-dihydroxybenzene. If an allergic reaction occurs, antihistamines should be used. The choice of antifungal drugs depends entirely on the clinical course of the disease and the individual characteristics of the patient's body.
What other types of foot fungi are there?
Foot candidiasis
This type of fungus occurs much less frequently in patients than epidermophytosis or erythromycosis. Pathology occurs under the influence of Candida fungi. This microorganism lives in everyone's body, however, it is considered conditionally pathogenic. In other words, they are not a threat in small amounts, but their rapid reproduction can cause unpleasant symptoms and consequences. If hypothermia, overwork, or frequent stress causes a decrease in immunity, the fungus will begin to multiply uncontrollably. External factors include:
- Wearing uncomfortable shoes, especially in summer;
- Injured at home or at work;
- The skin of the feet is constantly immersed (the skin falls off due to prolonged exposure to water).
There are two types of foot candidiasis: hyperkeratosis and vesicular pustules. The first form of candidiasis is characterized by thickening of the stratum corneum. On it, fairly wide light brown grooves began to appear, peeling off continuously. For diagnostic purposes, exfoliation was performed and further studies found particles of Candida.

The sticky pustular form of candidiasis manifests as hyperemia (overcrowding of blood vessels), marked swelling, and maceration. The affected skin area is covered with pustules and small flat blisters. After the inflammatory process disappears, desquamation will occur. Only after the exact diagnosis is confirmed can an appointment be made for treatment. The choice of medicine for this type of blister foot fungus is based on individual circumstances. In most cases, systemic and local medications are shown.
Onychomycosis
This disease is a type of foot fungus, which is characterized by a fungal nail infection. You may be infected in public showers, saunas, bathrooms, swimming pools. Scales containing pathogenic microorganisms are easily separated from the nail plate and may remain on floors, carpets, mats, and unpainted benches. High humidity not only allows them to survive, but also promotes active reproduction, so the risk of infection is significantly increased.
Initially, the infection enters the epidermis of the foot, causing intense itching. In order to reduce the unpleasant feeling, the person starts to comb the infected area, but the situation will only get worse. The skin area affected by the fungus is covered with small scratches and cracks, and the microorganisms begin to spread and penetrate under the nail plate, after which they begin to multiply uncontrollably.
Severe diseases such as diabetes or HIV, impaired blood circulation, and nail trauma can greatly increase the risk of infection.
Onychomycosis is divided into 3 types:
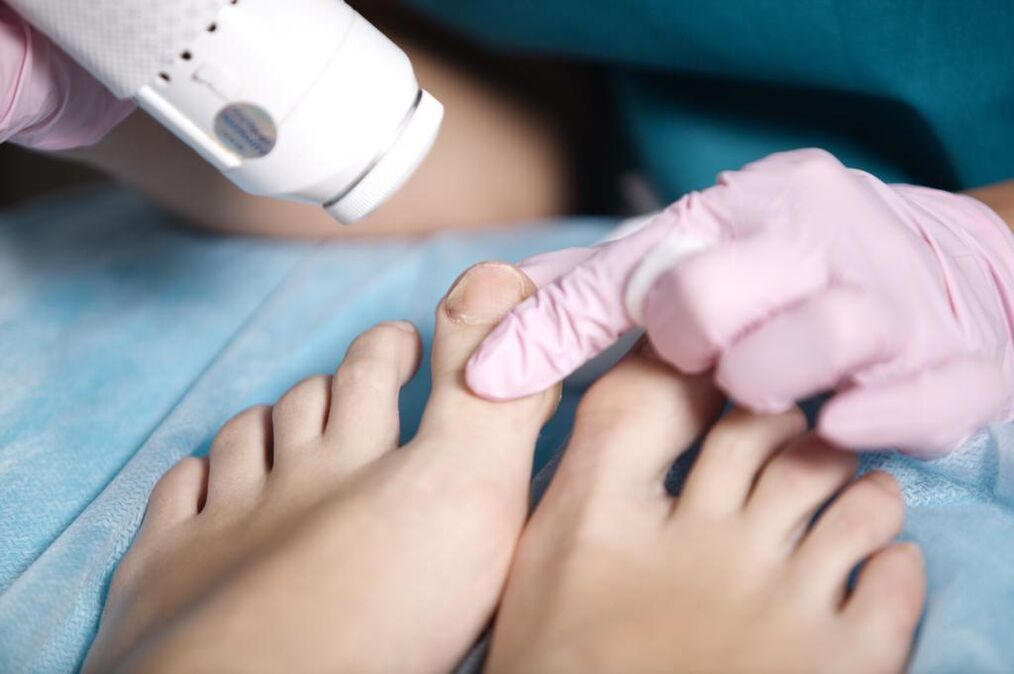
- Positive nutrition. For this type of onychomycosis, a change in nail color from normal to yellow-brown is observed. The natural luster, nail shape and thickness remain unchanged.
- Hypertrophy. The color of the nail will eventually change, its luster disappears, its shape changes, it thickens and begins to partially break down.
- Hyperthyroidism. The affected nails turned brown, thinned, and began to break. It began to gradually separate from the bed. In the open part of the nail bed, an uneven layer may be observed.
Because the spores of the fungus are located under the nails, it is ineffective to treat the fungus on the palms and feet with topical drugs. Before starting treatment, nails should be removed. This is done with stratum corneum separation drugs, and patches are also used. In some cases, it is possible to remove nails mechanically: use a nail file or pliers to cut off nail particles that have disappeared. It is important to remember that all instruments used must be sterile.
The combination of mechanical removal and cuticle separation patch is the most effective way to remove diseased nails. From the keratolytic agent, you can use a ready-made set, which contains a special ointment, a file for scraping nails, and a plaster. After removing the nail plate, you should start taking systemic antifungal drugs.
It is difficult to determine the type of foot fungus from the photos.
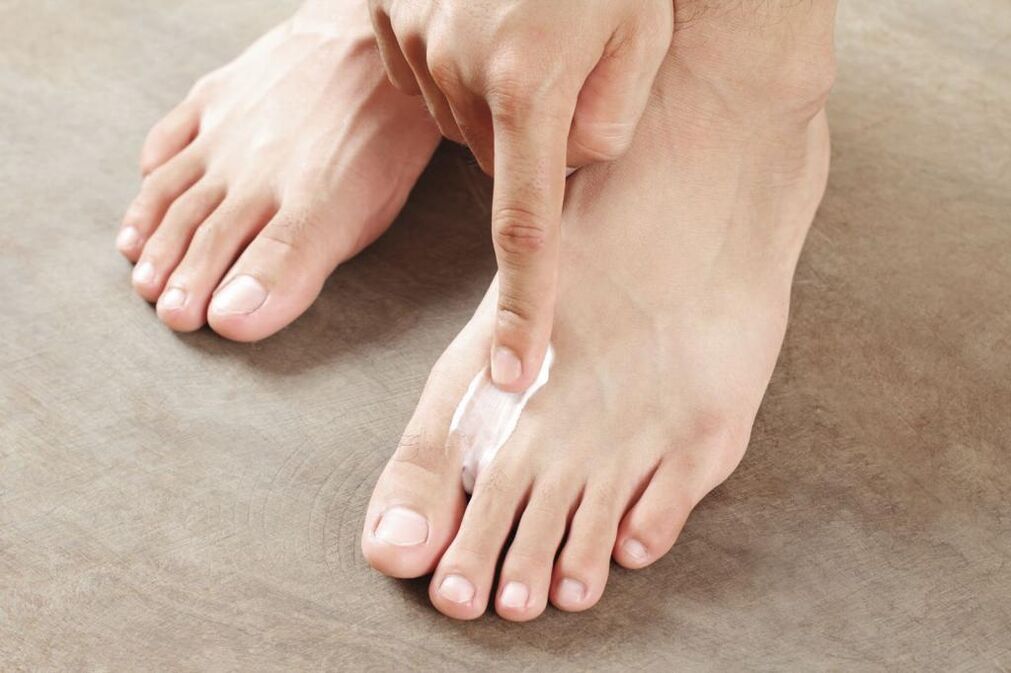
Intertriginous form
The most common and unpleasant type of pathology is the bruised form of fungal infection. It often occurs in summer and begins to develop between the third and fourth toes. Over time, the lesion spreads to the area between other fingers.
At first, a small crack, funnel, or sore will appear in the folds between the fingers. It is surrounded by diaper rash or greenish flaky skin. In most cases, the damaged area will get wet and sometimes pus will ooze from it. The erasure-type fungus is characterized by obvious or floury peeling, as if there is flour on the surface of a finger. A similar impression is created due to the large number of affected scales separated from the skin. There is slight itching and will not cause serious discomfort.
With the advanced form of the disease, the nails are stratified, severely thickened, with multiple cracks, and the stratum corneum is compacted like corns, and it is obviously yellow.
In rare cases, weeping-type disease-an exudative fungus. The main difference is that the vesicles fall into the affected area-bubbles filled with liquid. Treatment should be carried out in an integrated manner. Antifungal agents are used as external agents. The advanced form of the disease involves the use of systemic antifungal drugs. The treatment process should continue until the fungus has completely disappeared.
Squamous hyperkeratosis form
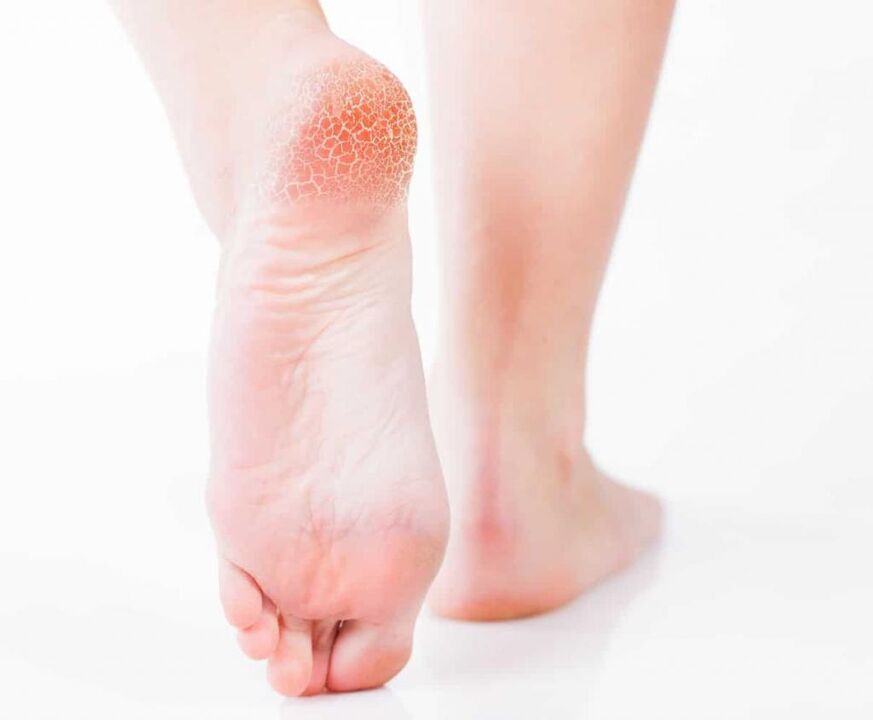
This type of foot fungus (shown in the picture below) is not common.
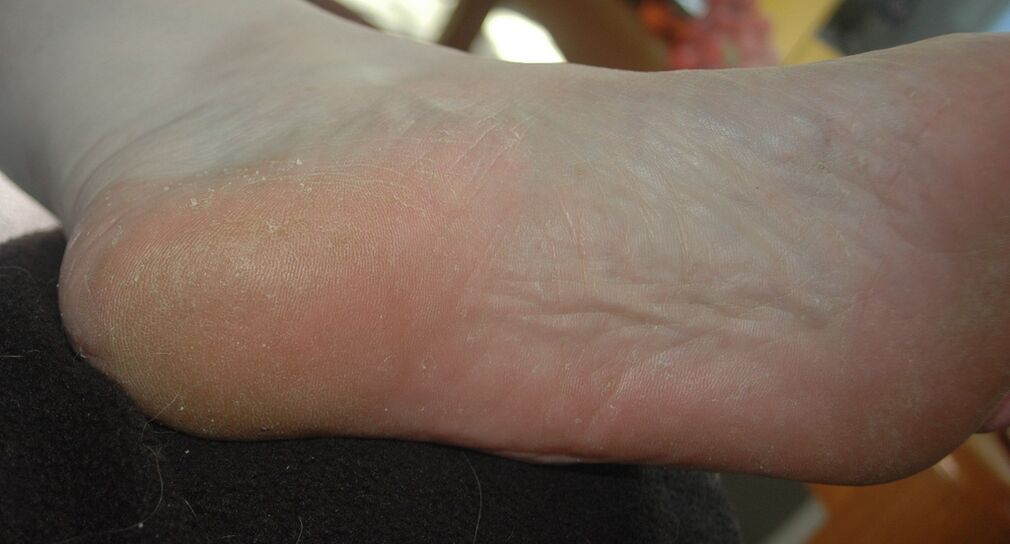
Scaly disease is the process by which pathogenic fungi invade the outer skin cells. Hyperkeratosis is the formation of the stratum corneum, which leads to thickening of the dermis. In this regard, the squamous hyperkeratosis form of mycosis has several names, for example, "buckskin fungus" and "beriberi".
Squamous hyperkeratosis mycosis is characterized by the following symptoms:
- The soles of the feet are covered with a thickened stratum corneum, giving the impression of wearing moccasins on the feet.
- The roughening of the sole occurred so strongly that it began to be covered with wide and thick calluses.
- Painful cracks appeared in the corn.
- The peeling is mucus-like, and the patterns on the skin are visible to the naked eye.
- There is unbearable itching.
- Over time, the nails begin to thin, break and chip.
When treating moccasin fungus, it is important to remove the stratum corneum of the skin first. This is done by using soap soda foot baths, wraps, salicylic acid dressings and ichthyol ointment. The dosage of salicylic acid ointment is as high as 10%. Vaseline cream and ointment containing lactic acid are both effective. If you cannot complete this task at home, you should seek help from a podiatry center. With the help of hardware manicure, experts will carefully exfoliate the keratinized dermis.
Follow-up treatment for the type of foot fungus will depend on the type of pathogen. It should only start after an accurate diagnosis has been made. It is not recommended to treat moccasin mycosis without first removing the stratum corneum of the skin-the active ingredients in the pharmaceutical composition will not be able to penetrate it and reach the focal point of infection. As a result, all efforts will be in vain.
A photo of the type of foot fungus does not fully reflect all the unpleasant symptoms experienced by a person.
Dehydrated form
Blister fungus, or also known as sweaty fungal disease, is the rarest type of disease. Its main manifestation is that many vesicles are combined into clumps. Vesicles are vesicles filled with pus or nutrient fluid from the inside. When the fluid begins to become cloudy, the vesicles rupture and the ulcer remains in place. They began to merge into a line, forming a visible scar on the skin. This is due to the drying and peeling of the skin layer.
Approximately 70% of vesicular fungal infections are accompanied by an allergic rash. Various bacteria and viruses began to invade the ulcer. As a result, diseases become mixed, and identification of initial pathogens becomes more difficult. Therefore, as soon as the main symptoms appear (pictured), you should immediately consult a doctor: he can quickly identify the type of foot fungus and start treatment.
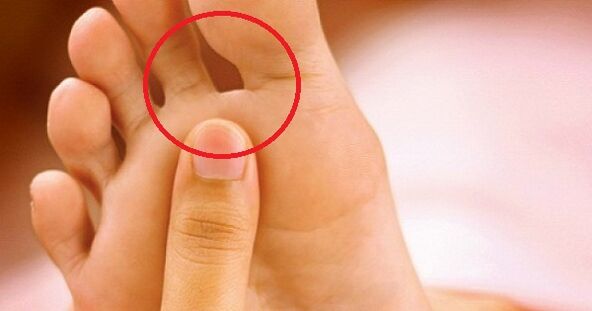
This should be done immediately. First, before using antifungal drugs, the acute process should be eliminated. It is best to entrust this task to an expert: he will be able to gently pierce the vesicles, treat the remaining ulcers with 2% boric acid, and apply a bright green solution or methylene blue.
Treatment of the disease in a neglected form involves the use of corticosteroid ointments. After eliminating the inflammatory process, topical antifungal agents are recommended. This will suppress the pathogen of the disease.
We continue to consider the name and type of foot fungus.
Erasure form
Mycosis in the erased form is almost invisible and its symptoms are minimal. These include: mild itching, burning, mucus-type peeling, and microcracks in the area between the fingers. If you do not consult a specialist when the first signs of the disease appear, the pathology may evolve into onychomycosis, which is more difficult to treat. In this case, the peeled nails will grow from one month to six months.
Use topical preparations to treat fungal diseases in the form of erasure: ointments, creams, foams. They allow you to form a layer on your feet to prevent other infections. It is not recommended to wash your feet within 24 hours after using these drugs.
Only in extreme cases can a prescription for systemic treatment be prescribed. The problem is that these drugs are toxic and can negatively affect certain internal organs, such as the liver. Therefore, if the use of topical therapy is effective, it is best not to take drugs.
Treatment of foot fungus types with alternative methods
The pathological photos displayed in the article will not cancel the itinerary to see the doctor.
Choosing drugs is easy now. However, many people prefer to treat the fungus with folk remedies. We offer several proven recipes:
- Clean your feet. The legs are heated in a basin of hot water, thoroughly wiped with laundry soap, and treated with a stiff foot brush for five minutes. The foam is rinsed off. Repeat the action 4-5 times. Then dry your feet and apply cream.
- Celandine bath. Pour 50 grams of herbs into 1. 5 liters of boiling water, heat for 4-5 minutes on the fire, and cool. The feet should be placed in the warm broth for 30 minutes. The course of treatment is 14 days.
- Tea tree oil is a powerful preservative. The affected area must be wiped repeatedly.
- You can use sour cream to remove itching and cracks. She lubricates her legs before going to bed. The duration of treatment is 1 week.
- baking soda. Eliminate skin burning and itching. Mix the powder with water to obtain a thick mass. Apply it to the affected area, wait for it to dry, and then rinse it off.
- Calendula. Pour the flowers (50 g) into boiling water (1: 2), hold for 30 minutes, and filter. Lubricate your feet with an infusion at night.

prevention
The simplest preventive measures will significantly reduce the likelihood of infection. Only personal items should be used, and the nails should be treated with sterile instruments. When going to public places such as baths, saunas, swimming pools, and beaches, you should use your own shoes. By the way, try to choose it so that it is comfortable and allows your legs to breathe.
Take precautions in advance to avoid various types of foot fungus in the future. This picture is far from all options for disease development.